Fasting during Ramadan is more than just a spiritual practice; it offers numerous health benefits backed by scientific research. One of the most significant advantages is its role in weight management. From improving metabolism to enhancing fat burning, fasting and weight loss are closely linked. By restricting food intake during specific hours, the body is forced to switch its energy source from glucose to stored fat, leading to effective weight loss. Additionally, fasting helps regulate hormones such as insulin and leptin, which play a crucial role in hunger control and fat storage. In this article, we will explore why fasting in Ramadan is good for your health, with a particular focus on its weight loss benefits, supported by research-backed discussions and practical insights.
Fasting and Weight Loss: How Ramadan Helps Shed Extra Pounds
Fasting in Ramadan promotes natural weight loss by:
- Encouraging fat burning as the body uses stored energy.
- Enhancing metabolic flexibility, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight.
- Improving insulin sensitivity, which reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes. (Patterson et al., 2015) Studies show that intermittent fasting, such as that observed during Ramadan, can significantly reduce body weight and fat mass while preserving muscle. (Sadeghirad et al., 2016)
Detoxification and Improved Digestion
One of the major benefits of fasting in Ramadan is its ability to detoxify the body. When fasting, the body shifts from constant digestion to a state of cellular repair. During this period:
- The liver breaks down toxins, flushing them out of the system.
- The gut gets time to rest, reducing inflammation and promoting a healthier digestive system.
- Autophagy, a natural process where the body cleans out damaged cells, is activated, reducing the risk of chronic diseases. (Mizushima et al., 2008)


Heart Health and Cholesterol Regulation
Another reason why fasting in Ramadan is good for your health is its impact on cardiovascular well-being. Research indicates that:
- Fasting lowers bad cholesterol (LDL) and increases good cholesterol (HDL). (Kul et al., 2014)
- Blood pressure levels stabilize, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Fasting decreases inflammation, a key contributor to heart-related conditions. By adopting a balanced diet during Suhoor and Iftar, one can further optimize heart health benefits.
Improved Brain Function and Mental Clarity
The mental benefits of fasting in Ramadan are often overlooked. Fasting:
- Promotes the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which supports cognitive function and memory. (Mattson et al., 2017)
- Reduces oxidative stress, which is linked to neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
- Enhances mood regulation by balancing neurotransmitters, reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Boosted Immune System and Reduced Inflammation
Studies reveal that fasting strengthens the immune system by:
- Encouraging the production of white blood cells, essential for fighting infections. (Longo & Mattson, 2014)
- Reducing chronic inflammation, which is linked to various diseases, including cancer and arthritis.
- Enhancing gut microbiota, leading to better digestion and nutrient absorption.
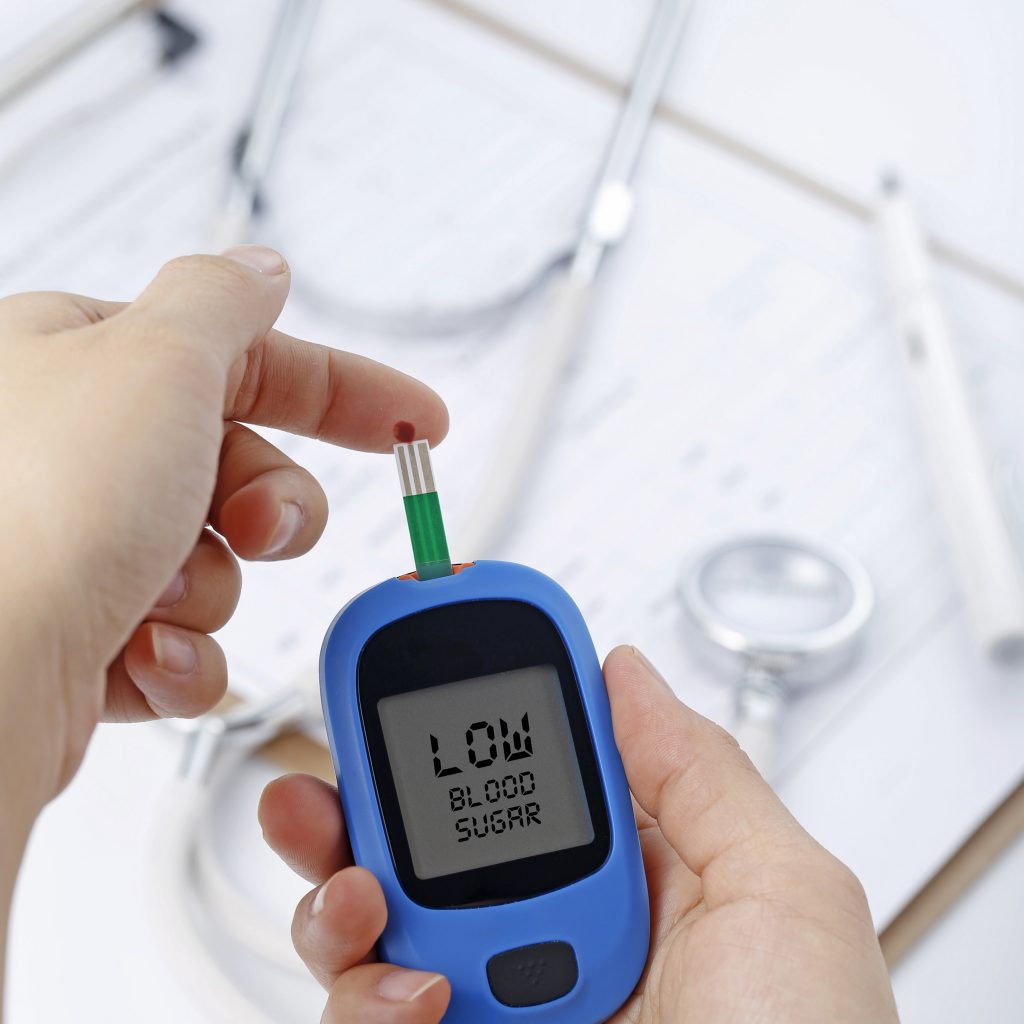
Blood Sugar Control and Diabetes Prevention
For those at risk of type 2 diabetes, fasting in Ramadan offers significant benefits:
- It stabilizes blood sugar levels by reducing insulin resistance.
- It prevents excessive calorie intake, which can contribute to metabolic disorders.
- A study by (Norouzy et al., 2013) found that Ramadan fasting led to better glycemic control in healthy individuals and those with prediabetes.
Psychological Well-being and Emotional Stability
The holistic approach of Ramadan fasting includes not only physical benefits but also psychological improvements:
- Fasting reduces cortisol levels, decreasing stress and anxiety.
- It enhances self-discipline, improving emotional regulation and mindfulness.
- Engaging in spiritual activities alongside fasting fosters inner peace and mental well-being.
Longevity and Anti-Aging Effects
Scientific research suggests that fasting can extend lifespan and slow aging:
- It promotes autophagy, which helps remove damaged cells and prevent age-related diseases.
- It increases human growth hormone (HGH), which plays a role in cell repair and longevity. (Rafael de Cabo et al., 2019)
- Studies on intermittent fasting suggest that those who fast regularly have a lower risk of premature aging.

How to Maximize the Health Benefits of Fasting in Ramadan
To make the most of fasting in Ramadan, consider these practical tips:
- Stay Hydrated – Drink plenty of water during non-fasting hours to prevent dehydration.
- Eat Nutrient-Dense Foods – Include whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in Suhoor and Iftar meals.
- Avoid Processed and Sugary Foods – These can spike blood sugar and lead to energy crashes.
- Exercise Wisely – Engage in light exercises such as walking or yoga to maintain physical activity.
- Get Enough Sleep – Prioritize rest to support metabolism and cognitive function.
Conclusion
The connection between fasting and weight loss in Ramadan is backed by science and experience. From detoxifying the body to improving brain function, the benefits extend far beyond just shedding extra pounds. By practicing mindful eating, staying hydrated, and maintaining a balanced lifestyle, you can optimize the health rewards of fasting. If done correctly, fasting in Ramadan can serve as a powerful reset for both body and mind.
References
- Mizushima, N., Yoshimori, T., & Levine, B. (2008). “Methods in Mammalian Autophagy Research.” Cell, 140(3), 313-326.
- Patterson, R. E., et al. (2015). “Intermittent fasting and human metabolic health.” Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 115(8), 1203-1212.
- Sadeghirad, B., et al. (2016). “The effect of Ramadan fasting on weight loss.” Obesity Reviews, 17(7), 735-745.
- Kul, S., et al. (2014). “Impact of Ramadan fasting on blood lipids and blood pressure.” Nutrition, 30(11-12), 1314-1320.
- Mattson, M. P., et al. (2017). “Intermittent metabolic switching and neuroplasticity.” Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 19(2), 63-80.
- Longo, V. D., & Mattson, M. P. (2014). “Fasting: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications.” Cell Metabolism, 19(2), 181-192.
- Norouzy, A., et al. (2013). “Ramadan fasting and blood sugar control.” Journal of Fasting and Health, 1(2), 69-74.
- Rafael de Cabo, M. P. (2019). “Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease.” New England Journal of Medicine, 381(26), 2541-2551.
Did you find this guide helpful? Share your thoughts in the comments!